Chap.4 Effects of solar wind on planets and satellites
4.1 Super rotation of Venus and inverted rotational axis of Venus
4.1.1 Rotation of Venus had inverted by meteorites from the Sun
The orbit and the rotation are usually in the same direction. But Venus
is rotating very slowly in the clockwise direction while orbiting counterclockwise
direction. There is the explanation that Venus collided with other planet
and the axis of rotation was reversed. But the orbit of Venus is closest
to the true circle. It is hard to reverse of the axis of rotation by a
collision. The material emitted by the fusion explosion of the Sun possesses
the counterclockwise directional angular momentum owing to the Sun’s rotation.
When the materials hit the Venus directly, the materials gave the torque
which rotates Venus clockwise Venus.
4.1.2 Superrotation of Venus has been driven by the solar wind
Venus has a slightly smaller mass than Earth, but its atmospheric pressure
is 90 times higher than Earth's. On the other hand, the solar wind is 350
to 900 km/sec with a rotation of 1.89 km/sec and collides with Venus. When
the solar wind with an anticlockwise rotation component due to the rotation
of the Sun hits the Venus' atmosphere in daytime hemisphere, the clockwise
directional air flow, i.e. superrotation of which speed is 100 m/s, is
driven by the solar wind via a gear mechanism.
Fig.9 shows a model of the effect of solar wind on Venus' atmosphere.
Fig.2(a) shows the morning side of Venus' daytime hemisphere, and (b) shows
the evening side of Venus' daytime hemisphere. On the daytime hemisphere,
the solar wind with counterclockwise rotation collides to the atmospheres
of Venus. So, the superrotation of clockwise rotation is driven. The shape
of the air flow becomes 90-degree counter-clockwise tilt of the Y shape.
On the other hand, on the east of Venus, the passing solar wind is the
opposite of the super-rotation, so there is a wrinkle of the flow on the
dawn side. In Fig.2(c), the air flow of the left side that is counterclockwise
flow is driven by the solar wind passes through east side of Venus. But
the right side of air flow is the superrotation that is the clockwise flow
driven by the daytime hemisphere.
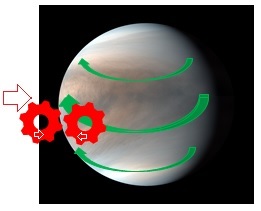
(a) Effect of solar wind at morning (b) Effect of solar wind at afternoon
(c) Effect of solar wind at night
Fig.9 Atomospheric flow of Venus, ( Source https://www.space.com/31325-venus-photos-by-japan-akatsuki-spacecraft.html )
4.1.3 Verifications of quantitative effects of solar wind on Venus
Approximates the amount of H+ emitted by the Sun as (MH+ from Sun) from Sun is (MH+ from Sun)=109 kg/sec,
and a part of this amount of H+ collides to Venus. The part is estimated by the ratio (γ) of area. Here,
spherical area with a radius of the distance from the Sun to Venus' orbit
(i.e. 1.08x108 km) is (SV sphere= 13.6x1016). Venus cross-sectional area (SVenus) is SVenus =π(6,052)2 =π (3.662x107)2.
Then the ratio (γ) is γ = (1.15x108 /13.6x1016) =0.846x10-9.(1.15x108 /13.6x1016) = 0.846 x10-9.
So the mass of H+ that collides to the Venus is 0.846 kg/s.
Since the solar wind of 0.846 kg/s has rotational velocity of 1.89 km/s
due to rotational motion of the Sun, the rotational energy of the Sun (K rotation) is given by Krotation= (1/2) Mv2 = 0.423x3.57x106 = 1.
51x106 J/sec Assuming that the average speed of 600 km/sec, the energ of striking
solar wind (Kstrike) that is added to Venus is given by Kstrike = (1/2) Mv2 = 0. 423x36x1010
= 1. 52x1011 J/sec. The momentum of the solar wind that has been accumulated for 4
billion years will be accumulated by 40x108x365x24x3600=1.26x1017
times. Therefore, the rotational energy of solar wind that is accumulated
for 4 billion years is about 1. 9x1023 J. The total energy of the transfer
movement of the solar wind accumulated for 4 billion years is 1.91x1028 J.
On the other hand, the uniform sphere moment of inertia (I) is given by
I=(2/5)M r2. and Venus mass M=4.87×1024 kg, Venus radius r=6.052x106m, and the moment of inertia (I) is I = (2/5)Mr2 =7.13x1037.
Since rotational period of Venus is 243days, the rotational angular velocity of the rotation is
given by ω= 2π/(243x24x3600) = 3.0x10-7rad/sec So, the total rotational
energy is K Venus’s rotation=0.5x7.133x1037(x(3x10-7)2 ≒3,2×1024. But the rotational period
of Venus must be changed. Here, assuming that early Venus had the same
rotation angular velocity of the Earth's rotation, the rotation angular
velocity is ω=2π/(24x3600) = 7.26x10-5 rad/sec. The energy of motion is
K Earth’s rotation= (1/2) Vω2= 0.5x7.133x1037x(7.26x10-5)2≒1.88×1029 J.
This value is 10 times of the momentum of the transfer movement of the
solar wind that accumulated for 4 billion years is 1.91x1028 J. The assumption that Venus had rotated initially nearly same as Earth
was not correct. It is considered that Venus is thought to have increased of its mass due
to the material emitted by the Sun by the Sun's fusion explosion at the
end stage ofVenus's formation.In other words,it is considered that Venus' rotation had reversed by the collision of
material emitted from the Sun in the lend stage of Venus's formation. The period of Mercury's rotation
is 59 days, and That of Mars' rotation is 24.63 hours. The Mercury rotates
very slowly compared with that of Mars. That is It is considered that Mercury's
rotation had slow down by the collision of material emitted from the Sun
by the Sun's fusion explosion at the end stage of Mercury’s formation.
index -4.1-